The research project SISI has its roots in the fundamental study PESI (FFG no. 845219), which indicated that the integration of industrial excess energy into the energy supply of a town is feasible and has the potential of covering an essential part of the final energy demand. SISI aimed at developing a comprehensive plan for increased cooperation and energy exchange between the city and the industry. In contrast to the state-of-the-art, which considers the integration of large amounts of industrial waste heat as problematic, costly and neglects other industrial energy potentials, the project SISI considered industrial excess energy as an essential source of energy for achieving the goal of a regional and renewable energy supply of Judenburg.
SISI – Smart City Judenburg through synergies with the industry

-
Project duration:01/04/2016 – 31/03/2017
The project SISI illustrates a town‘s quest to become a Smart City through the use of industrial energy combined with regional and renewable energy sources.
Project Objectives
One of the project objectives was the integration of industrial excess energy (waste heat, waste water, waste or roof surfaces for PV systems). The project illustrated that industrial energy can make a significant contribution to the energy supply of an urban area and partly replace fossil fuels in the process. Another positive side effect is the reduction of CO2 emissions and decreased dependence on energy imports. The full energy supply of Judenburg through regional and renewable energy was another project goal of SISI.
Based on regional development plans and an analysis of available potential of industrial and regional renewable energy, energy goals, indicators and different scenarios for energy development were developed. As a next step, the feasibility of the scenarios was assessed through extensive simulations. In order to provide realistic cost and profitability assessments an appropriate selection of technologies was also taken into account.
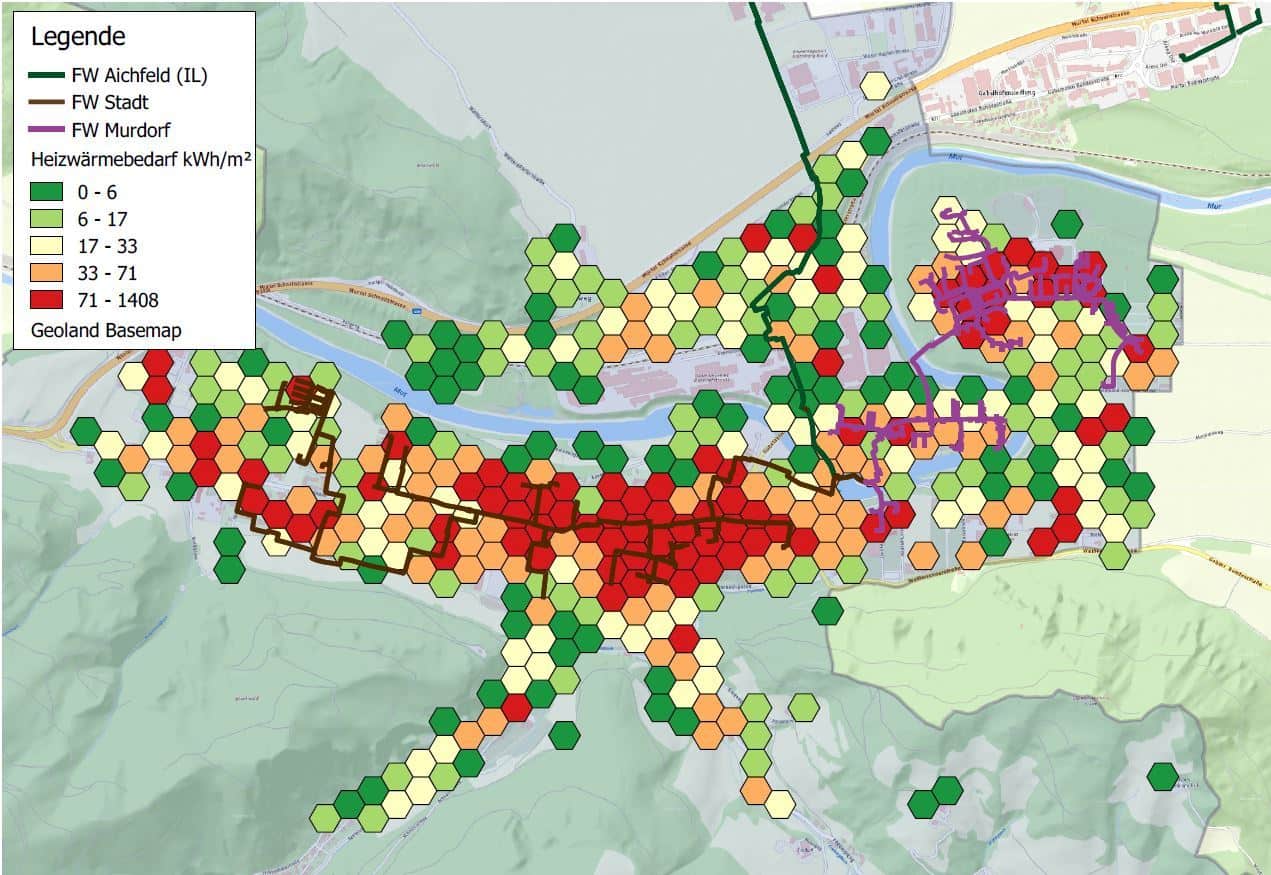
Photo: FH JOANNEUM
Heating requirements and district heating grids of Judenburg

Project Results
The results show that industrial energy can make a significant contribution to the energy supply of a city. Including regional, renewable energy sources, the share of renewable energy in the field of electricity can be increased to 100 % and 62 % in the field of heating (based on annual energy amounts). When considering time characteristics of supply and demand, the percentages decline to cover ratios of 57 % for electricity and 47 % for heat.
Based on the project results the following recommendations were made:
- Establishment of a company for the implementation of innovative integrated energy projects.
- Increased marketing of Judenburg, a modern and future-oriented city of energy.
- Installation of PV systems on public roofs, residential buildings, commercial and industrial roofs.
- Installation of heat pumps in industrial plants to use the waste water potential and feed the district heating grid.
- Installation of heat exchangers in industrial plants to use waste heat of flue gas and feed the district heating grid.
- Conversion from fossil to biogenic heating systems in private homes in areas which cannot be supplied by district heating.
After the successful project completion in spring 2017, the city of Judenburg is currently reviewing the recommendations and putting them into action. At the moment, there are intensive talks between the city and selected companies in order to use the potential of low-temperature waste heat. The installation of heat pumps can produce acceptable heat levels and makes the supply of the district heating grid possible.